【导读】
地面塌陷作为一种极具隐蔽性和难预测性的地质灾害,给建筑、交通等基础设施以及人员安全带来了严重威胁。分布式光纤传感技术(DFOS)凭借其独特的优势,正在成为地面塌陷监测领域的重要手段。本文深入探讨了DFOS技术的基本原理,详细对比了其相较于传统监测技术的显著优势,如抗电磁干扰、耐腐蚀、高灵敏度以及能够实现长距离连续监测等。通过回顾地面塌陷光纤监测技术的研发历程、基于实测数据的塌陷灾变机理研究以及该技术在实际工程中的应用情况,全面展示了DFOS在地面塌陷监测中的适用性和创新价值。同时,文章也客观分析了当前DFOS技术在地面塌陷监测应用中面临的瓶颈问题,如传感器适应性不足、解调稳定性和可靠性有限、智能化分析能力欠缺等,并进一步指出了未来的研究热点方向,包括新型传感器研发、解调技术改进、数据智能化处理以及多技术融合等。总之,本文为读者呈现了DFOS技术在地面塌陷监测领域的全景图,既展示了其广阔的应用前景,也明确了未来需要攻克的技术难关。
【研究背景】
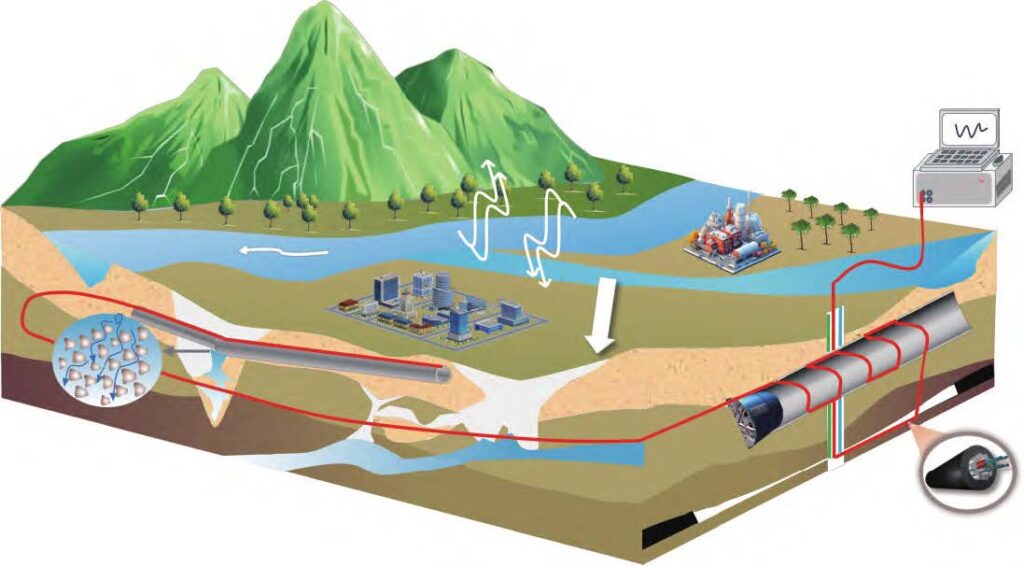
地面塌陷是一种常见的地质灾害,通常由自然因素或人类活动引发。随着城市化进程的加速,人为活动导致的地面塌陷灾害事故日益增多。这种灾害不仅威胁建筑、地铁隧道和公路等基础设施的安全,还可能导致大量人员伤亡。地面塌陷的形成过程具有隐蔽性和难以预测性,可能表现为缓慢变形或迅速发展为大范围快速塌陷,因此需要高精度的实时监测来降低其对人类生产生活的影响。传统监测技术如遥感、地理信息系统、地球物理方法等在测量范围和精度等方面存在局限性。例如,遥感技术虽然覆盖区域广,但数据采集频率受限且无法获取地表以下信息;地理信息系统擅长数据管理与分析,但对实时监测与动态变化捕捉能力不足;地球物理方法在探测地下空洞等方面有一定优势,但受现场条件限制大,且成本较高。这些技术难以满足地面塌陷精细化监测的需求,尤其是在长距离、大范围和长周期监测方面存在明显不足。
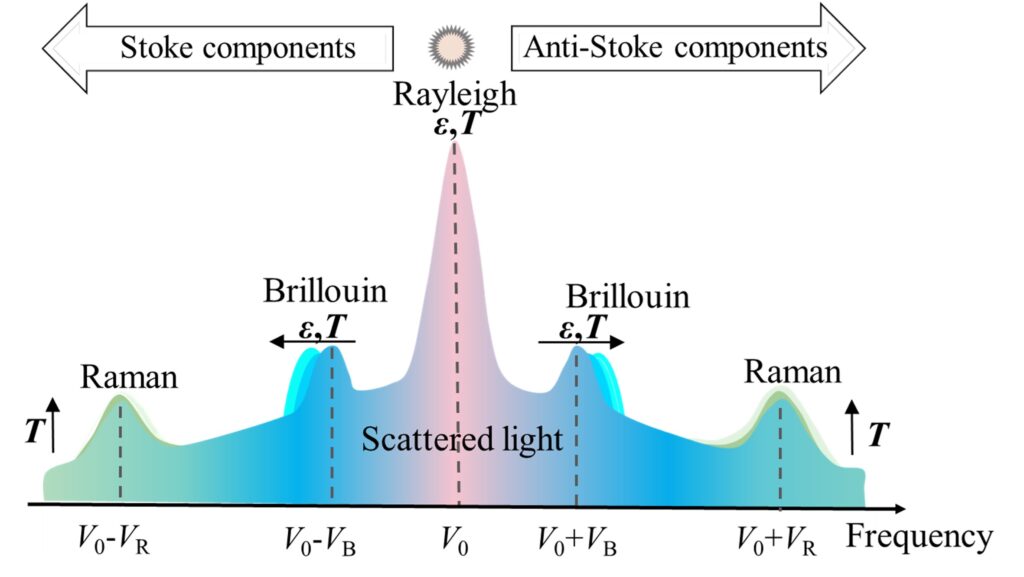
图1 光纤中的散射光
分布式光纤传感技术(DFOS)的发展为地面塌陷监测提供了新的解决方案。如图1所示,该技术通过在时域或频域内利用瑞利散射、拉曼散射或布里渊散射原理,能够测量温度、应力、应变和其他声学特性等参数。DFOS技术具有抗电磁干扰、耐腐蚀、灵敏度高且可实现长距离连续监测等显著优势,适用于长距离、大范围和长周期的地质体监测。近年来,DFOS技术在结构健康监测、地质灾害预警与防治以及环境监测等领域得到了广泛应用,成为各类地质工程分布式监测的重要手段。
【主要内容】
近年来,随着城市化进程的不断加快,地面塌陷这一隐蔽而破坏性强的地质灾害逐渐引起各界关注。作为一项前沿技术,分布式光纤传感(DFOS)凭借其全程连续、高精度、实时监测和抗干扰等显著优势,正在推动地面塌陷监测技术的深度革新。
地面塌陷光纤监测技术研发
在地面塌陷光纤监测技术研发方面,DFOS系统的构建不仅涉及高灵敏度传感器的选择,还对光缆与土体之间的力学耦合关系提出了新的要求。首先,传感光缆作为监测系统的“神经中枢”,其选用直接关系到数据采集的稳定性和精度。科研团队通过对单模和多模光纤的优劣比较,结合实际岩土环境条件,探索出适合长距离、连续监测的传感光缆。如图2所示,在拉拔试验中,界面一般经历由黏结摩擦到局部破坏、再到全面脱黏的渐进性破坏过程,通过在光缆表面添加锚固结构,可以增强缆-土变形协调性并更好地捕捉土体局部应变集中区域。该模型不仅为光缆锚固和界面增强提供了理论依据,而且通过实验验证,证实了增大围压、优化锚固点设计等手段可以显著提高光缆与土体之间的耦合性能。此外,在光纤应变数据向位移转化的建模过程中,通过结合积分运算和人工神经网络等先进算法,研发出多种应变—位移转换模型,极大地提升了地面沉降预测的精度和实时响应能力。这些技术突破为DFOS系统在复杂地质环境下的可靠部署奠定了坚实的基础,也为日后灾害预警和风险评估提供了有效的数据支撑。
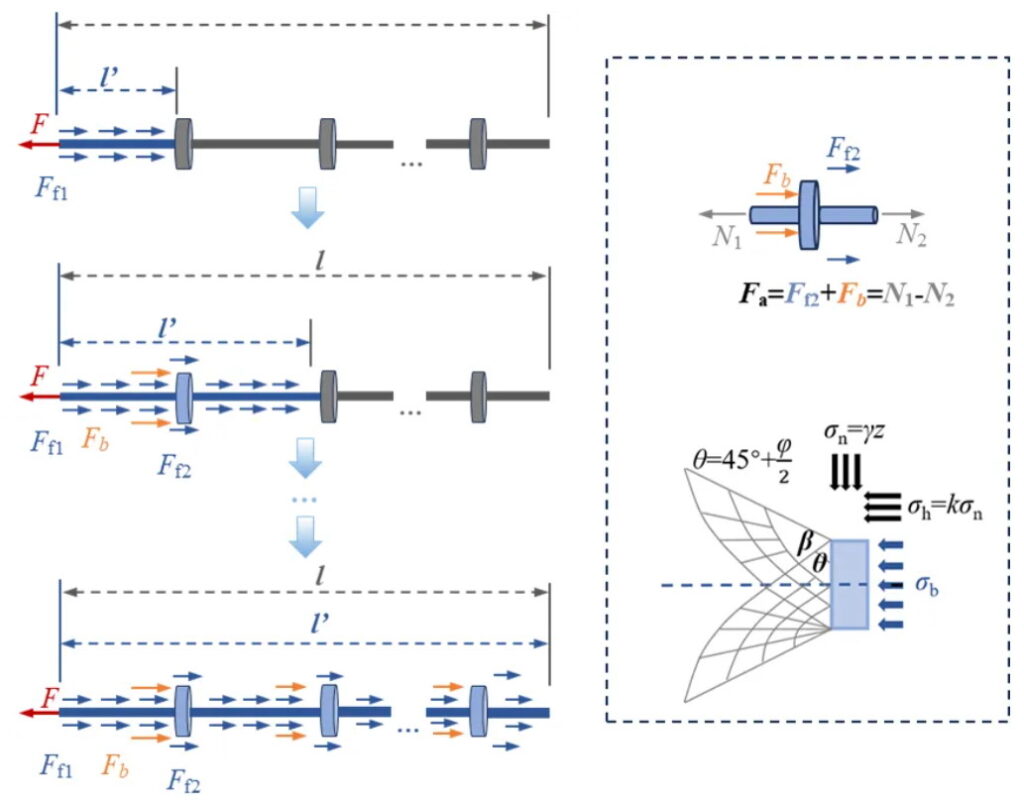
图2 锚固光缆与土体相互作用示意图
基于实测的塌陷灾变机理研究
在塌陷灾变机理研究中,DFOS技术展现出其独特的优势。通过在实验室和现场的多种模拟试验,研究人员利用DFOS系统捕捉到地面塌陷过程中的微小应变变化,实现了从空洞初期形成、扩展到地表失稳全过程的动态监测。例如,通过采用BOFDA、OFDR等光纤信号解调技术,不仅实现了应变信号的精确采集,还揭示了塌陷过程中的“马鞍型”横向应变分布和“台阶状”竖向应变分布特征。实验结果表明,在地下空洞逐步扩展过程中,上覆土体会形成局部土拱结构以暂时抵抗塌陷风险,而这一过程中应变信号的集中区域和变化速率为灾害预警提供了关键参考。结合粒子图像测速(PIV)技术和小波分解算法,研究人员进一步优化了现场数据处理流程,有效提取了关键应变参数,实现了从数据采集到机理解析的无缝衔接。
地面塌陷光纤监测的工程应用研究
在工程应用层面,DFOS技术已经在多个复杂环境下成功落地,展现出极高的实用价值。以岩溶、管道泄漏以及煤矿采空区沉陷等实际案例为例,工程界通过布设DFOS系统,实现了对大范围、多层次地面沉降的实时、连续监测。通过与GIS平台的深度融合,该监测系统不仅能够实时采集海量应变数据,还能进行数据智能化分析与可视化展示,从而准确圈定塌陷区域,提升了灾害预警的时效性和准确性。实际应用中,通过BOTDR、ϕ-OTDR、FBG等多种光纤传感技术的综合应用,研究者不仅成功捕捉到了地表微小沉降信号,而且利用监测数据重构了土体变形模型,为后续工程安全评估和风险控制提供了有力的技术支持。尤其在管道泄漏引发的局部沉降监测中,通过主动分布式温度传感技术(ADTS)等新型手段,系统能够准确定位泄漏点及其扩展范围,实现对隐蔽性较强的地下结构的有效监控。与此同时,煤矿采空区沉陷的全断面监测也借助DFOS技术的高灵敏度和空间分布式优势,实现了从覆岩变形到地表沉降全过程的精准捕捉。如图3所示,当地下形成采空区时,上覆岩层的弯曲变形会在光纤中引起不同的拉应变或压应变区。通过对这一分布式应变数据进行分析,可以较为准确地推算地表沉降量及裂隙发展趋势。
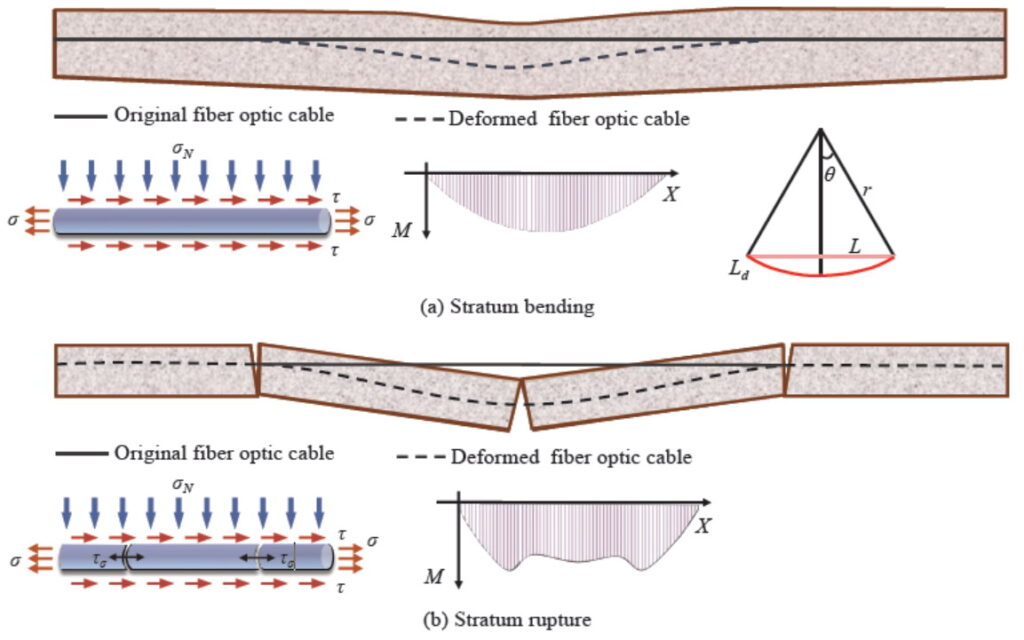
图3 岩层变形光纤监测模型
【结论】
分布式光纤传感技术(DFOS)在地面塌陷监测中的应用已展现出诸多优势,但未来仍有广阔的发展前景和提升空间。首先,随着新型传感器技术的不断涌现,针对不同地质环境和监测需求的光纤传感器将进一步优化,提升数据采集的精度与稳定性。其次,针对光缆与土体耦合性问题的研究仍需深化,通过多物理场耦合模型和现场试验,探索更高效的界面加固和锚固技术,为实际工程提供更加可靠的监测依据。与此同时,结合人工智能和大数据技术,对海量应变数据进行智能化处理和实时预警,将极大提高灾害风险评估的准确度。此外,多种监测技术的融合应用(如DFOS与GNSS、InSAR等技术的联合监测)也将成为未来研究的重要方向,从而实现对地面塌陷全过程的综合、多尺度监控。
来源:红外与激光工程, 2025, 54(4): 20250120. DOI: 10.3788/IRLA20250120
作者:任绪言1,朱鸿鹄1,2,高宇新1,谭道远1,2
单位:1.南京大学 地球科学与工程学院,2.江苏省大地感知与控灾工程研究中心
全文链接:http://irla.cn/article/doi/10.3788/IRLA20250120
Review of Research on Ground Subsidence Monitoring Based on Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing
Ren Xu-yan1, Zhu Hong-hu1,2*, Gao Yu-xin 1, Tan Dao-yuan1,2
(1. School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
- Jiangsu Engineering Research Center of Earth Sensing and Disaster Control, Nanjing 210023, China)
Abstract:
Significance Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS) technology plays a crucial role in ground collapse monitoring, enabling real-time detection of surface settlement, crack development, and underground structural deformation. It provides essential support for geological hazard early warning and safety assessment. Through a systematic elaboration of the fundamental principles of DFOS technology and its performance advantages over traditional monitoring techniques—such as anti-electromagnetic interference, corrosion resistance, high sensitivity, and long-distance continuous monitoring—combined with the development of ground collapse fiber-optic monitoring technologies, research on collapse disaster mechanisms based on measured data, and engineering application studies of ground collapse fiber-optic monitoring, the applicability and innovative value of this technology are demonstrated. Furthermore, this study analyzes the challenges of DFOS in ground collapse monitoring, including sensor adaptability issues, demodulation stability and reliability are limited, and insufficient intelligent data analysis capabilities. Finally, future research hotspots are identified.
Progress Significant progress has been made in ground collapse monitoring using distributed fiber optic sensing (DFOS). Technically, DFOS, based on Rayleigh, Brillouin, and Raman scattering, enables high – precision measurement of temperature, stress, and strain, supporting long – distance, large – scale, and long – term geological monitoring (Fig. 3, Fig. 5, Fig. 6). Professor Zhu Honghu’s team at Nanjing University developed a three – stage mechanical model for interfacial stress transfer, revealing the progressive failure and strain evolution of the fiber – soil interface (Fig. 8). Various strain – to – displacement models, such as Chen’s BOTDR – based model and Gao’s ANN – modified model, have enhanced monitoring accuracy.
In application, DFOS is used in karst collapse, pipeline – induced collapse, mining – related collapse, and tunnel – related collapse, aiding disaster early – warning and safety assessment (Fig. 10, Fig. 13, Fig. 15). For instance, in karst collapse monitoring, DFOS captures strain signals during cave expansion, supporting risk warning. In pipeline – induced collapse monitoring, it monitors pipe deformation post – leakage to reflect collapse conditions. In mining – related collapse monitoring, DFOS captures dynamic characteristics of overlying strata deformation and surface subsidence. In tunnel – related collapse monitoring, its high precision and anti – interference capability make it a key tool.
Moreover, the integration of DFOS with other monitoring methods in multimodal perception systems improves data accuracy and monitoring range. Intelligent algorithms further optimize disaster identification and early – warning capabilities.
Conclusions and Prospects This paper reviews the latest advancements in Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS) technology for ground subsidence monitoring, highlighting its ability to capture subtle surface and subsurface changes for high-precision, real-time monitoring and risk warning in scenarios such as karst collapse, pipeline leakage, and mining subsidence. By leveraging optical scattering principles, DFOS has shown significant advantages in long-distance, wide-area monitoring. However, challenges in environmental adaptability, data demodulation accuracy, and intelligent analysis still exist. For example, in harsh underground conditions, maintaining stable performance of fiber-optic sensors is difficult. Data demodulation is easily affected by environmental noise, leading to potential inaccuracies. Looking ahead, advancements in new fiber materials, multimodal monitoring integration, and intelligent algorithm applications are expected to enhance the efficiency and reliability of DFOS systems. The development of robust fiber materials can improve sensor durability in complex environments. Integrating multimodal monitoring methods, such as combining DFOS with InSAR and GNSS, will provide more comprehensive and accurate data. Furthermore, the application of intelligent algorithms based on machine learning and big data analytics can significantly boost data processing efficiency and the accuracy of risk warnings, thus offering more precise and effective support for geological disaster prevention.
Key words: distributed fiber optic sensing (DFOS); ground collapse; deformation; early warning
Funding projects: National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42225702, 4241101112)
引用格式:任绪言, 朱鸿鹄, 高宇新, 等. 地面塌陷分布式光纤监测技术研究综述(特邀)[J].红外与激光工程, 2025, 54(4): 20250120. DOI: 10.3788/IRLA20250120
参考文献:
- TAN Y, LONG Y Y. Review of cave-in failures of urban roadways in China: A database[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2021, 35(6): 04021080.
- CLOSSON D, Structural control of sinkholes and subsidence hazards along the Jordanian Dead Sea coast[J]. Environmental Geology, 2005, 47(2): 290-301.
- SUN Wanming. Stability analysis of surface subsidence area caused by multi-level filling mining in a gold mine[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2024, 33(7): 216-225. (in Chinese) 孙万明. 某金矿多中段充填开采对地表塌陷区稳定性影响分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2024, 33(7): 216-225.
- ZHANG Feng, DIAO Xinpeng, TAN Xiuquan, et al. Exploration and stability evaluation of coal mine goaf based on SBAS technology[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(3): 208-214.(in Chinese) 张丰, 刁鑫鹏, 谭秀全, 等. 基于SBAS技术的煤矿采空区探查与稳定性评价[J].煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(3): 208-214.
- YAO Yuchun, LI Anhong, ZHOU Bo, et al. Analysis on key technologies of high -speed railway subgrade in karst foundation[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2023, 40(8): 35-39. (in Chinese) 姚裕春, 李安洪, 周波, 等. 岩溶地基高速铁路路基关键技术分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2023, 40(8): 35-39.
- WU Di, LI Aiai, LI Dan, et al. Simplified design method of reinforcement treatment for karst subgrade collapse[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(3): 538-547.(in Chinese) 吴迪, 李艾文, 李丹, 等. 岩溶路基加筋防塌治理的简化设计方法[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(3): 538-547.
- GAO Y X, ZHU H H, SU J W, et al. Experimental study on deformation and failure mechanism of geogrid-reinforced soil above voids[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2025, 53: 203-216
- WEI Chao, ZHU Honghu, GAO Yuxin. Model test study of ground collapse using distributed fiber optic sensing[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(9): 2443-2456. (in Chinese) 韦超, 朱鸿鹄, 高宇新,等. 地面塌陷分布式光纤感测模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2022, 43(9): 2443-2456.
- GAO Y X, ZHU H H, Wei C, et al. Performance evaluation of distributed strain sensing nerves for monitoring ground collapse: A laboratory study[J]. Measurement, 2023, 217: 113100.
- GAO Y X, ZHU H H, QIAO L, LIU X F, WEI C. Feasibility study on sinkhole monitoring with fiber optic strain sensing nerves[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 15(11): 3059-3070.
- PLATTNER C, WDOWINSKI S, DIXON TH, et al. Surface subsidence induced by the Crandall Canyon Mine (Utah) collapse: InSAR observations and elasto-plastic modelling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2010, 183(3): 1089-1096.
- WU Yuanbin, Liu Zhikui, YIN Renchao, et al. Evaluation of karst collapse susceptibility in Huaihua area,Hunan Province based on AHP and GIS[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(1): 21-33. (in Chinese) 吴远斌, 刘之葵, 殷仁朝, 等. 基于AHP和GIS技术的湖南怀化地区岩溶塌陷易发性评价[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(1): 21-33.
- ZHENG Zhijie, CHEN Yixiang, GAN Fuping. Brief analysis of the geophysical properties of rock and soil in karst area-taking Geely karst collapse area as an example[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2016, 31(2): 920-927. (in Chinese) 郑智杰, 陈贻祥, 甘伏平. 岩溶区岩土层地球物理性质浅析-以吉利岩溶塌陷区为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016, 31(2): 920-927.
- LEUCCI G, GIORGI L D. Microgravimetric and ground penetrating radar geophysical methods to map the shallow karstic cavities network in a coastal area (Marina Di Capilungo, Lecce, Italy) [J]. Exploration Geophysics, 2010, 41(2): 178-188.
- GÓMEZ-ORTIZ D, MARTÍN-CRESPO T. Assessing the risk of subsidence of a sinkhole collapse using ground penetrating radar and electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Engineering Geology, 2012, 149-150: 1-12.
- WANG D Y, ZHU H H, SHI B, et al. Performance monitoring of a curved shield tunnel during adjacent excavations using a fiber optic nervous sensing system[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022, 124: 104483.
- YE X, ZHU H H, WANG J, et al. Subsurface multi-physical monitoring of a reservoir landslide with the fiber-optic nerve system[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(11): e2022GL098211.
- SHA Te, LUO Yong, LEI Kunchao, et al. Comprehensive monitoring of land subsidence and ground fissures in Songzhuang, Beijing, based on distributed optical fiber sensing technology. Geological Bulletin of China, 2024, 43(5): 859−867. (in Chinese) 沙特, 罗勇, 雷坤超, 等. 基于分布式光纤传感技术的北京宋庄地面沉降和地裂缝综合监测[J]. 地质通报, 2024, 43(5): 859-867.
- WU B, ZHU H H, CAO D F, et al. Fiber optic sensing-based field investigation of thermo-hydraulic behaviors of loess for characterizing land–atmosphere interactions[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 315: 107019.
- SHI B, ZHANG C C, FANG K, et al. Soil stratum tides[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2023, 50(1): e2022GL101621
- SHI Bin, ZHU Honghu, ZHANG Chengcheng, et al. Rock and soil disaster sensing and application[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2023, 53(10): 1639-1651. (in Chinese) 施斌, 朱鸿鹄, 张诚成, 等. 岩土体灾变感知与应用[J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2023, 53(10): 1639-1651.
- WU B, ZHU H H, CAO D F, et al. Feasibility study on ice content measurement of frozen soil using actively heated FBG sensors[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2021, 189: 103332.
- TAN X, FAN L, et al. Detection, visualization, quantification, and warning of pipe corrosion using distributed fiber optic sensors[J]. Automation in Construction, 2021, 132: 103953.
- WANG D Y, ZHU H H, Wang J, et al. Characterization of sliding surface deformation and stability evaluation of landslides with fiber–optic strain sensing nerves[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 314(5): 107011.
- LIU Wei, ZHU Honghu, ZHANG Hanyu, et al. Feasibility study of seismic events positioning based on distributed acousticsensing array[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2023, 54(5): 1804−1813. (in Chinese) 刘威, 朱鸿鹄, 张汉羽, 等. 基于分布式声波传感阵列的地震动事件定位可行性研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 54(5): 1804-1813.
- CHEN Z, ZHANG C C, SHI B, et al. Eavesdropping on wastewater pollution: Detecting discharge events from river outfalls via fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Water Research, 2024, 250: 121069.
- MOTIL A, BERGMAN A, TUR M. State of the art of Brillouin fiber-optic distributed sensing[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2016, 78: 81-103.
- SHE Junkuan, ZHU Honghu, ZHANG Chengcheng, et al. Experiment study on mechanical properties od interface between sensing optical fiber and sand[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(5): 855-860. (inChinese) 佘骏宽, 朱鸿鹄, 张诚成, 等. 传感光纤-砂土界面力学性质的试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(5): 855-860.
- ZHU H H, SHE J K, ZHANG C C, et al. Experimental study on pullout performance of sensing optical fibers in compacted sand [J]. Measurement, 2015, 73: 284-294.
- ZHANG C C, ZHU H H, SHI B, et al. Interfacial characterization of soil-embedded optical fiber for ground deformation measurement[J]. Smart Material Structures, 2014, 23: 095022.
- ZHANG C C, ZHU H H, SHE J K, et al. Quantitative evaluation of optical fiber/soil interfacial behavior and its implications for sensing fiber selection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(5): 3059-3067.
- CHEN Dongdong, ZHU Honghu, ZHANG Chengcheng, et al. Experimental study on strain sensing optical fiber-soil linterfacial properties considering influence of embedment length[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(4): 1027-1034. (in Chinese) 陈冬冬, 朱鸿鹄, 张诚成, 等. 考虑埋入长度效应的应变传感光纤-土体界面特性试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(4):1027-1034.
- ZHANG C C, ZHU H H, SHI B. Role of the interface between distributed fibre optic strain sensor and soil in ground deformation measurement[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 36469.
- ZHANG C C, ZHU H H, SHI B, et al. Performance evaluation of soil embedded plastic optical fiber sensors for geotechnical monitoring[J]. Smart Structures and Systems, 2016, 17(2): 297-311.
- ZHU Honghu, SHI Bin, YAN Junfan, et al. Physical model testing of slope stability based on distributed fiber-optic strain sensing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(4): 821-828. (in Chinese) 朱鸿鹄, 施斌, 严珺凡, 等. 基于分布式光纤应变感测的边坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(4): 821-828.
- LI Huanqiang, SUN Hongyue, LIU Yongli, et al. Application of optical fiber sensing technology to slope model test[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(8): 1703-1708. (in Chinese) 李焕强, 孙红月, 刘永莉, 等. 光纤传感技术在边坡模型试验中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, (8): 1703-1708.
- CHENG G, SHI B, ZHU H H, et al. A field study on distributed fiber optic deformation monitoring of overlying strata during coal mining[J]. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2015, 5(5): 553-562.
- ZHANG C C, ZHU H H, CHEN D D, et al. Feasibility Study of an chored fiber-optic strain-sensing arrays for monitoring soil deformation beneath model foundation[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2019, 42(4): 966-984.
- ZHANG C C, ZHU H H, LIU S P, et at. Quantifying progressive failure of micro-anchored fiber optic cable-sand interface via high-resolution distributed strain sensing [J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2020, 57(6): 871-881.
- ZHU H H, GAO Y X, CHEN D D, et al. Interfacial behavior of soil-embedded fiber optic cables with micro-anchors for distributed strain sensing[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2024, 19: 1787-1798.
- CHEN H J, HE J P, XUE Y, et al. Experimental study on sinkhole collapse monitoring based on distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensor[J]. Optik, 2020, 216: 164825.BUCHOUD E, VRABIE V, et al. Quantification of submillimeter displacements by distributed optical fiber sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation And Measurement, 2016, 65(2): 413-422.
- LU Yi, YU Jun, GONG Xulong, et al. Experimental study on distributed monitoring of ground collapse deformation based on BOFDA[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2018, 24(5): 778-786. (in Chinese) 卢毅, 于军, 龚绪龙, 等. 基于BOFDA的地面塌陷变形分布式监测模型试验研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2018, 24(5): 778-786.
- GUAN Zhende, JIANG Xiaozhen, GAO Ming. A calibration test on optical fiber sensing device for karst collapse monitoring[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2012, 31(2): 173-178+197. (in Chinese) 管振德, 蒋小珍, 高明. 岩溶塌陷光纤传感试验装置的标定试验[J]. 中国岩溶, 2012, 31(2): 173-178+197.
- LINKER R, KLAR A, ASCE M. Detection of sinkhole formation by strain profile measurements using BOTDR: simulation study[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 143(3): B4015002
- GAO Y X, ZHU H H, SU J W, et al. Investigating soil arching evolution in dense sand via fully instrumented trapdoor tests[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2024, 19: 6055-6071.
- JIANG Xiaozhen, LEI Mingtang, CHEN Y, et al. An experiment study of monitoring sinkhole collapse byusing BOTDR optical fiber sensing technique[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2006, (6): 75-79. (in Chinese)蒋小珍, 雷明堂, 陈渊, 等. 岩溶塌陷的光纤传感监测试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2006, (6): 75-79.
- JIANG X Z, GAO Y L, WU Y B, LEI M T. Use of Brillouin optical time domain reflectometry to monitor soil-cave and sinkhole formation[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75: 225.
- HONG Rubao, JIAN Wenbin, CHEN Xuezhen. Study on response of covered karst soil cave to groundwater changes and its collapse evolution process[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2023, 31(1): 240-247. (in Chinese)洪儒宝, 简文彬, 陈雪珍. 覆盖型岩溶土洞对地下水升降作用的响应及其塌陷演化过程研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2023, 31(1): 240-247.
- GUTIERREZ F, SEVIL J, SEVILLANO P et al. The application of distributed optical fiber sensors (BOTDA) to sinkhole monitoring. Review and the case of a damaging sinkhole in the Ebro Valley evaporite karst (NE Spain) [J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 325: 107289.
- HAO Wenjie, YANG Zhuojing, ZHANG Qing, et al. Application of optical fiber sensing techniques to karst collapse[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(1): 134-137. (in Chinese)郝文杰, 杨卓静, 张青,等. 光纤传感技术在岩溶塌陷监测中的应用研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(1): 134-137.
- He J P, Xue Y, Xu J, et al. Whole-process monitoring of sinkhole collapse based on distributed optical fiber strain-vibration joint system and its case study in railway subgrade[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2020, 60: 102380
- XU Hongzhong, ZHOU Yuan, ZHANG Dan. Development of karst collapse monitoring system using distributed optical fiber sensor based on GIS[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(3): 120-123. (in Chinese)徐洪钟, 周元, 张丹. 基于GIS的岩溶塌陷分布式光纤监测系统的研发[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2011, 38(3): 120-123.
- XU J, HE J P, ZHANG L. Collapse prediction of karst sinkhole via distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensor[J]. Measurement, 2017, 100: 68-71.
- MÖLLER T, BURKE T S, XU X M, et al. Distributed fibre optic sensing for sinkhole early warning: experimental study[J]. Géotechnique, 2023,73(8): 701-715.
- RAGIONE G D, BILOTTA E, XU X M, et al. Numerical investigation of fibre-optic sensing for sinkhole detection[J]. Géotechnique, 2024, 74(12): 1329-1342.
- CHENG L, PAN P S, SUN Y K, et al. A distributed fibre optic monitoring method for ground subsidence induced by water pipeline leakage[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2023, 81: 103495
- GUO S, SHAO Y, ZHANG T Q, et al. Physical modeling on sand erosion around defective sewer pipes under the influence of groundwater[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 139(12): 1247-1257.
- INDIKETIYA S, JEGATHEESAN P, RAJEEV P. Evaluation of defective sewer pipe–induced internal erosion and associated ground deformation using laboratory model test[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal. 2017, 54(8): 1184-1195.
- KWAK T Y, WOO S I, KIM J, et al. Model test assessment of the generation of underground cavities and ground cave-ins by damaged sewer pipes[J]. Soils and Foundations. 2019, 59(3): 586-600.
- SATO M, KUWANO R. Influence of location of subsurface structures on development of underground cavities induced by internal erosion[J]. Soils and Foundations. 2015, 55(4): 829-840.
- LI H J, ZHU H H, TAN D Y, et al. Detecting pipeline leakage using active distributed temperature Sensing: Theoretical modeling and experimental verification[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2023, 135: 105065.
- SUN Mengya, SHI Bin, DUAN Xinchun, et al. Experimental study on the feasibility and influencing factors of pipeline leakage monitoring based on FBG[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2019, 39(5): 715-723. (in Chinese) 孙梦雅, 施斌, 段新春, 等. 基于FBG的管道渗漏监测可行性及其影响因素试验研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2019, 39(5): 715-723.
- SUN M Y, SHI B, ZHANG D, et al. Pipeline leakage monitoring experiments based on evaporation‐enhanced FBG temperature sensing technology[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2021, 28(3): e2691.
- LI H J, ZHU H H, WU H Y, et al. Experimental investigation on pipe-soil interaction due to ground subsidence via high-resolution fiber optic sensing[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022, 127: 104586.
- WANG Deyang ZHU Honghu, WU Haiying, et al. Experimental study on buried pipeline instrumented with fiber optic sensors under ground collapse[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(6): 1125-1131. (in Chinese) 王德洋, 朱鸿鹄, 吴海颖, 等. 地层塌陷作用下埋地管道光纤监测试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(6): 1125-1131.
- ZHANG Z J, WANG C, TANG Y X, et al. Analysis of ground subsidence at a coal-mining area in Huainan using time-series InSAR[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36: 5790-5810.
- LI Fengming, DING Xinpin, SUN Jiakai. Ecological environment status and development trend of governance technology of coal mining subsidence area in China[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(11): 232-239. (in Chinese)李凤明, 丁鑫品, 孙家恺. 我国采煤沉陷区生态环境现状与治理技术发展趋势[J]. 煤矿安全, 2021, 52(11): 232-239.
- ZHANG Y, LU W X, YANG Q C. The impacts of mining exploitation on the environment in the Changchun – Jilin – Tumen economic area, Northeast China[J]. Natural Hazards, 2015, 76(2): 1019-1038.
- CHAI Jing, OUYANG Yibo, ZHANG Dingding, et al. Theoretical analysis of the mechanical coupling between rock and optical fiber for distributed sensing of overlying strata deformation[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering, 2020, 2(3):73-82. (in Chinese) 柴敬, 欧阳一博, 张丁丁, 等. 采场覆岩变形分布式光纤监测岩体-光纤耦合性分析[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报, 2020, 2(3): 73-82.
- CHAI J, LEI W L, DU W G, et al. Experimental study on distributed optical fiber sensing monitoring for ground surface deformation in extra-thick coal seam mining under ultra-thick conglomerate[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2019, 53: 102006.
- CHAI J, MA Z, ZHANG D D, et al. Experimental study on PPP-BOTDA distributed measurement and analysis of mining overburden key movement characteristics [J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2020, 56: 102175.
- FANG Xing, LIU Jiankui. Application of distributed optical fiber sensing technology in monitoring residual deformation in coal mining subsiding area[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology, 2016, 39(2): 260-264. (in Chinese) 方星, 刘建奎. 分布式光纤传感技术在采煤塌陷残余变形监测上的应用[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 39(2): 260-264.
- LUO Zhihui, HUA Peng, XU Bing, et al. Ground surface displacement monitoring method based on ultra-weak fiber Bragg grating array[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(S1): 18-24. (in Chinese) 罗志会, 华鹏, 徐冰, 等. 基于超弱光纤光栅阵列的地表位移监测方法[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(S1): 18-24.
- CAO Kai, WU Jianning, LU Yuan, et al. Distributed acoustic sensing monitoring of overburden fractures in coal mine goaf[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(6): 125-135. (in Chinese) 曹凯, 吴建宁, 卢渊, 等. 煤矿采空区覆岩破裂分布式声波传感监测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(6): 125-135.
- CAI Yi, SHEN Huazhang, HUANG Houxu, et al. Study on evolution law of internal deformation of soil mass corresponding to subsidence stretching area of thick loose layer mining areas: a case of Suntuan Coal Mine in Huaibei[J]. Coal Science And Technology, 2024, 52(8): 36-49. (in Chinese) 蔡毅, 沈华章, 黄厚旭, 等. 厚松散层矿区开采沉陷拉伸区域土体内部变形演化规律研究——以淮北孙疃煤矿为例[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024, 52(8): 36-49.
- ZHANG Pingsong, XU Shiang, FU Xianjie, et al. Internal deformation characteristics and full section monitoring for extremely thick loose layers under mining conditions[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(1): 628-644. (in Chinese) 张平松, 许时昂, 傅先杰, 等. 煤层采动巨厚松散层全断面监测及内部变形特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(1): 628-644.
- ZHANG Pingsong, SUN Binyang, XU Shiang, et al. Multi parameter monitoring technology of borehole for movement and deformation of overlying strata of coal measures[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(8): 2907-2922. (in Chinese) 张平松, 孙斌杨, 许时昂, 等. 煤系上覆地层移动变形钻孔多参数监测技术[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(8): 2907-2922.
- YE Shaomin. Application of deformation monitoring system in Beijing-Xiong’an intercity railway tunnel based on multiparameter optical fibersensing technology[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2021, 41(7) : 1141-1149. (in Chinese) 叶少敏. 基于多参量光纤传感技术的京雄城际隧道形位感测系统应用研究[J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2021, 41(7): 1141-1149.
- DONG Peng, XIA Kaiwen, YU Changyi, et al. Monitoring and analysis of stratum deformation and subsidence overlying a shallow tunnel using distributed optical fiber sensing technology[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2019, 39(5): 724-732. (in Chinese) 董鹏, 夏开文, 于长一, 等. 浅埋隧道覆岩变形沉降的分布式光纤监测与分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2019, 39(5): 724-732.
- ZHAO F C, LU X L, SHI H B, et al. Study on stratified settlement and weak reflectivity fiber grating monitoring of shield tunnel crossing composite strata[J]. Applied Sciences, 13(3): 1769.
- HOU Gongyu, XIE Bingbing, JIANG Yusheng, et al. Theoretical and experimental study of the relationship between optical fiber strain and settlement of roof based on BOTDR technology[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(5): 1298-1304. (in Chinese) 侯公羽, 谢冰冰, 江玉生, 等. 基于BOTDR的光纤应变与顶板沉降变形关系的模型构建与试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(5): 1298-1304.
- HOU Gongyu, LI Zixiang, HU Tao, et al. Study of tunnel settlement monitoring based on distributed optic fiber strain sensing technology[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(9): 3148-3158. (in Chinese) 侯公羽, 李子祥, 胡涛, 等. 基于分布式光纤应变传感技术的隧道沉降监测研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(9): 3148-3158.
- SONG H B, PEI H F, ZHU H H. Monitoring of tunnel excavation based on the fiber Bragg grating sensing technology[J]. Measurement, 2021, 169: 108334.
- LI Z X, HOU G Y, HU T, et al. Deformation behavior monitoring of a tunnel in its temporary shoring demolishing process using optical fiber sensing technology[J]. Measurement, 2021, 176: 109170.
- CHENG G, SHI B, ZHU H H, et al. A field study on distributed fiber optic deformation monitoring of overlying strata during coal mining[J]. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2015, 5: 553-562.
- MENG Yan, GUAN Zhende. A discussion on the key technical problem in monitoring andpredicting sinkhole with optical fiber sensing (BOTDR) technique[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(2): 187-192. (in Chinese) 蒙彦, 管振德. 应用光纤传感技术进行岩溶塌陷监测预报的关键问题探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(2): 187-192.
- CHENG Gang, WANG Zhenxue, SHI Bin, et al. Research progress of DFOS in safety mining monitoring of mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(8): 2923-2949. (in Chinese) 程刚, 王振雪, 施斌, 等. DFOS在矿山工程安全开采监测中的研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(8): 2923-2949.
- WU Haiying, ZHU Honghu, ZHU Bao, et al. Review of underground pipeline monitoring research based on distributed fiber optic sensing[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2019, 53(6): 1057-1070. (in Chinese) 吴海颖, 朱鸿鹄, 朱宝, 等. 基于分布式光纤传感的地下管线监测研究综述[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2019, 53(6): 1057-1070.
