作者:施斌1*, 王宝善2, 张诚成1, 顾凯1, 阮友谊1, 李广伟1, 王勤1, 魏广庆3, 张丹1, 朱鸿鹄1, 程刚1, 陈颙1
1. 南京大学地球科学与工程学院, 南京210023;
2. 中国科学技术大学地球和空间科学学院, 地震与地球内部物理实验室, 合肥230026;
3. 南京大学(苏州)高新技术研究院, 苏州215123
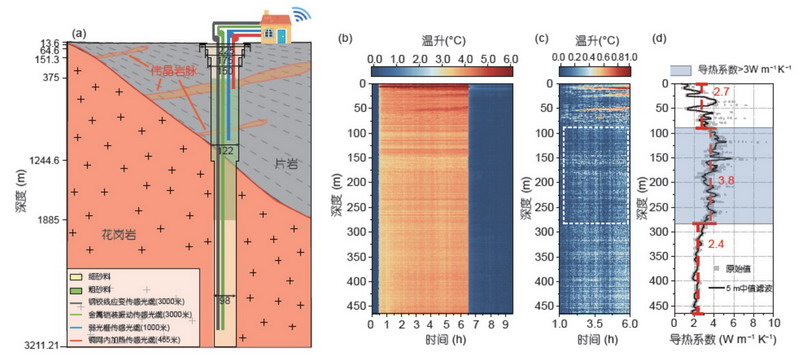
摘要:川西甲基卡锂矿3211 m科学深钻位于青藏高原东缘鲜水河断裂及川藏铁路附近, 是目前青藏高原上最深的科学钻孔. 利用此深钻观测深部物理场和浅部环境的变化过程, 对于研究青藏高原地壳活动、川藏铁路场地稳定性和生态环境保护等均具有重要意义. 采用分布式光纤传感(distributed fiber optic sensing, DFOS)技术, 我们研发了高强度、耐高温的特种传感光缆, 成功植入甲基卡锂矿深钻中, 建成了世界上海拔最高和深度最大的光纤观测孔, 实现了应变、温度、振动、水分等多物理量的分布式原位观测. 本文是甲基卡光纤观测孔第一阶段的成果, 包括岩体热导率的原位测定、钻孔回填过程的分布式声波振动(distributed acoustic sensing, DAS)观测、地震监测与地震成像等方面的初步进展. 研究表明: DFOS应用于深钻全断面多物理量观测是可行的, 它完全能适应深钻高温和高压的观测环境, 并具有长距离、实时、连续分布式观测的优势; 将分布式温度传感光纤、应变传感光纤和声波传感光纤集于一根传感光缆的设计思路保障了深钻传感光缆的安装质量, 并为DFOS技术应用于地球物理和地质工程的多物理场观测开辟了广阔的应用空间.
关键词:钻孔观测, 分布式光纤传感, 多物理量, 甲基卡, 地震监测
参考文献
1 Fu X F, Liang B, Zou F G, et al. Discussion on metallogenic geological characteristics and genesis of rare polymetallic ore fields in western Sichuan (in Chinese). Acta Geol Sin, 2021, 95: 3054–3068 [付小方, 梁斌, 邹付戈, 等. 川西甲基卡锂等稀有多金属矿田成矿地质特征与成因分析. 地质学报, 2021, 95: 3054–3068]
2 Zhang P Z. A review on active tectonics and deep crustal processes of the western Sichuan region, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics, 2013, 584: 7–22
3 Xiong T Y, Yao X, Zhang Y S. A review on study of activity of Xianshuihe fault zone since the Holocene (in Chinese). J Geomech, 2010, 16: 176–188 [熊探宇, 姚鑫, 张永双. 鲜水河断裂带全新世活动性研究进展综述. 地质力学学报, 2010, 16: 176–188
4 Fan X, Scaringi G, Korup O, et al. Earthquake-induced chains of geologic hazards: Patterns, mechanisms, and impacts. Rev Geophys, 2019, 57: 421–503
5 Xue Y G, Kong F M, Yang W M, et al. Main unfavorable geological conditions and engineering geological problems along Sichuan-Tibet railway (in Chinese). Chin J Rock Mech Eng, 2020, 39: 445–468 [薛翊国, 孔凡猛, 杨为民, 等. 川藏铁路沿线主要不良地质条件与工程地质问题. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39: 445–468]
6 Dong Y K, Li H. Current situation of borehole multi-component observation technology (in Chinese). Technol Earthq Disaster Prev, 2014, 9: 149–158 [董云开, 李宏. 井下综合观测技术发展现状. 震灾防御技术, 2014, 9: 149–158]
7 Chi S L. Deep-hole broad-band strain-seismograph and high-frequency seismology—The hope to successful earthquake prediction (in Chinese). Prog Geophys, 2007, 22: 1164–1170 [池顺良. 深井宽频钻孔应变地震仪与高频地震学——地震预测观测技术的发展方向, 实现地震预报的希望. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22: 1164–1170]
8 Shi B, Zhang D, Zhu H H. Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing for Geoengineering Monitoring (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 2019 [施斌, 张丹, 朱鸿鹄. 地质与岩土工程分布式光纤观测技术. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019]
9 Bense V F, Read T, Bour O, et al. Distributed temperature sensing as a downhole tool in hydrogeology. Water Resour Res, 2016, 52: 9259–9273
10 Zhang B, Gu K, Shi B, et al. Actively heated fiber optics based thermal response test: A field demonstration. Renew Sustain Energy Rev, 2020, 134: 110336
11 del Val L, Carrera J, Pool M, et al. Heat dissipation test with fiber-optic distributed temperature sensing to estimate groundwater flux. Water Res, 2021, 57: e2020WR027228
12 des Tombe B F, Bakker M, Smits F, et al. Estimation of the variation in specific discharge over large depth using distributed temperature sensing (DTS) measurements of the heat pulse response. Water Resour Res, 2019, 55: 811–826
13 Shi B, Zhang D, Zhu H, et al. DFOS applications to geo-engineering monitoring. Photonic Sens, 2021, 11: 158–186
14 Lellouch A, Yuan S, Spica Z, et al. Seismic velocity estimation using passive downhole distributed acoustic sensing records: Examples from the San Andreas Fault Observatory at depth. J Geophys Res Solid Earth, 2019, 124: 6931–6948
15 Booth A D, Christoffersen P, Schoonman C, et al. Distributed acoustic sensing of seismic properties in a borehole drilled on a fast-flowing Greenlandic outlet glacier. Geophys Res Lett, 2020, 47: e2020GL088148
16 Wang B S, Zeng X F, Song Z H, et al. Seismic observation and subsurface imaging using an urban telecommunication optic-fiber cable (in Chinese). Chin Sci Bull, 2021, 66: 2590–2595 [王宝善, 曾祥方, 宋政宏, 等.利用城市通信光缆进行地震观测和地下结构探测. 科学通报, 2021, 66: 2590–2595]
17 Kim H, Cho J W, Song I, et al. Anisotropy of elastic moduli, P-wave velocities, and thermal conductivities of Asan Gneiss, Boryeong Shale, and Yeoncheon Schist in Korea. Eng Geol, 2012, 147-148: 68–77
18 Maldaner C H, Munn J D, Coleman T I, et al. Groundwater flow quantification in fractured rock boreholes using active distributed temperature sensing under natural gradient conditions. Water Resour Res, 2019, 55: 3285–3306
19 Gou L, Zhang S H, Yu G, et al. Optical sensing promotes intelligence, innovation and development of reservoir geophysical technology (in Chinese). Pet Sci Technol Forum, 2021, 40: 55–64 [苟量, 张少华, 余刚, 等. 光纤传感推动油藏地球物理技术智能创新发展. 石油科技论坛, 2021, 40: 55–64]
20 Zhang C C, Shi B, Zhu H H, et al. Toward distributed fiber-optic sensing of subsurface deformation: A theoretical quantification of groundborehole-cable interaction. J Geophys Res Solid Earth, 2020, 125: e2019JB018878
21 Fang H, Yao H, Zhang H, et al. Direct inversion of surface wave dispersion for three-dimensional shallow crustal structure based on ray tracing: Methodology and application. Geophys J Int, 2015, 201: 1251–1263
22 Rawlinson N, Sambridge M. Wave front evolution in strongly heterogeneous layered media using the fast marching method. Geophys J Int, 2004, 156: 631–647
23 Jiang W, Xi C, Wang W, et al. Time window selection of seismic signals for waveform inversion based on deep learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5903610
引用格式: 施斌, 王宝善, 张诚成, 等. 川西甲基卡锂矿3211 m科学深钻多物理量分布式光纤观测. 科学通报, 2022, 67: 1–8
Shi B, Wang B S, Zhang C C, et al. Multi-physical distributed fiber optic observation in a 3211-m-deep scientific borehole at Jiajika lithium mine, western Sichuan (in Chinese). Chin Sci Bull, 2022, 67: 1–8, doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1380
