 随着城市化进程的加速,民用基础设施建设区域不断扩展,但新兴城市开发区常因缺乏详细的地质勘查资料和长期监测数据,面临较大的地质灾害风险。掌握地下多场信息的时空变化对保障工程建设安全和地下空间开发利用至关重要。在四川天府新区,南京大学朱鸿鹄教授团队利用一个新开发的光纤神经系统(FONS),获取了全面的地下多物理信息,涵盖了地层变形、温度和地表水文等数据。该系统整合了三种尖端的光纤传感技术:光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)、布里渊光时域反射(BOTDR)和拉曼光时域反射(ROTDR)。研究者们在9个监测钻孔中布设了全分布式和准分布式的应变/温度传感光缆,这些钻孔位置覆盖了平原、阶地以及活动断层带等多种不同的地质特征。现场监测数据充分验证,应用光纤神经系统对城市开发区进行地质勘探和监测是可行的。本研究为这一经济高效的技术未来在地质灾害防治领域的推广应用提供了参考依据。
随着城市化进程的加速,民用基础设施建设区域不断扩展,但新兴城市开发区常因缺乏详细的地质勘查资料和长期监测数据,面临较大的地质灾害风险。掌握地下多场信息的时空变化对保障工程建设安全和地下空间开发利用至关重要。在四川天府新区,南京大学朱鸿鹄教授团队利用一个新开发的光纤神经系统(FONS),获取了全面的地下多物理信息,涵盖了地层变形、温度和地表水文等数据。该系统整合了三种尖端的光纤传感技术:光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)、布里渊光时域反射(BOTDR)和拉曼光时域反射(ROTDR)。研究者们在9个监测钻孔中布设了全分布式和准分布式的应变/温度传感光缆,这些钻孔位置覆盖了平原、阶地以及活动断层带等多种不同的地质特征。现场监测数据充分验证,应用光纤神经系统对城市开发区进行地质勘探和监测是可行的。本研究为这一经济高效的技术未来在地质灾害防治领域的推广应用提供了参考依据。
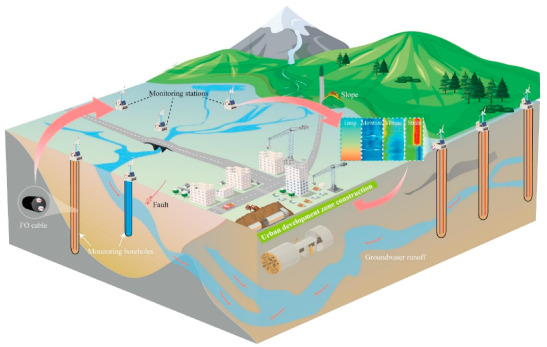
图 1.在城市开发区部署 FONS 进行现场监测
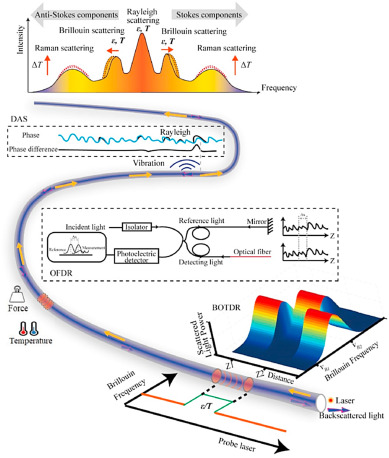
图 2.用于应变和温度传感的 DFOS 技术原理
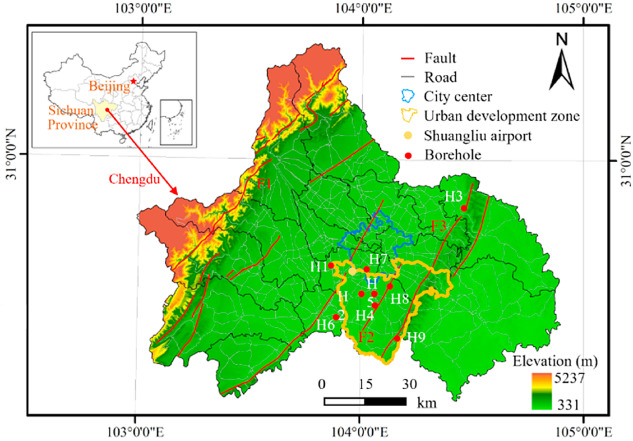
图 3.研究区的位置和监测孔
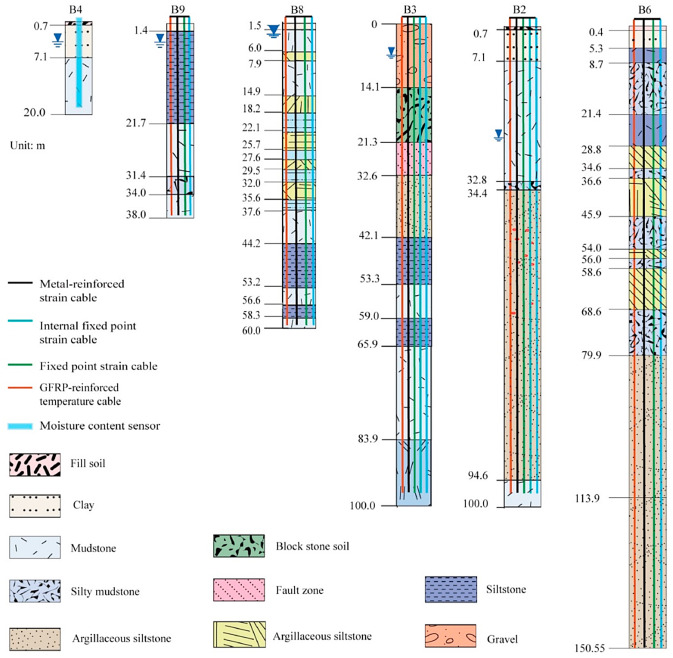
图 4.六个监测孔的地层剖面
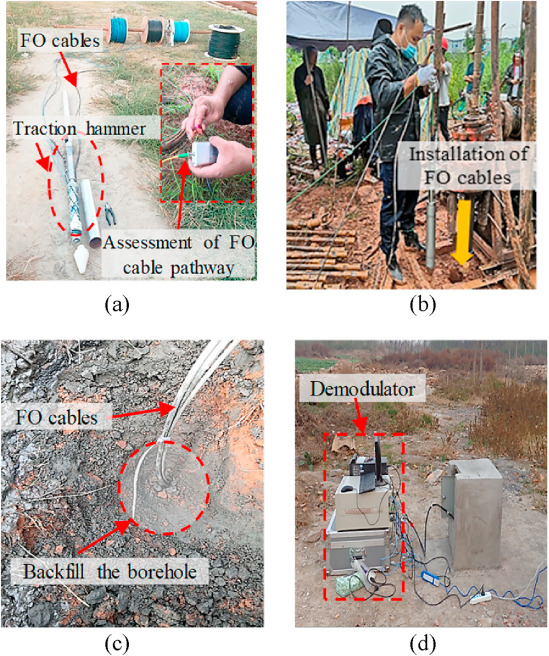
图 6.监测站施工照片:(a) 光缆安装的准备工作;(b) 将光缆放入钻孔中;(c) 回填钻孔;(d) 使用光纤解调仪进行数据采集
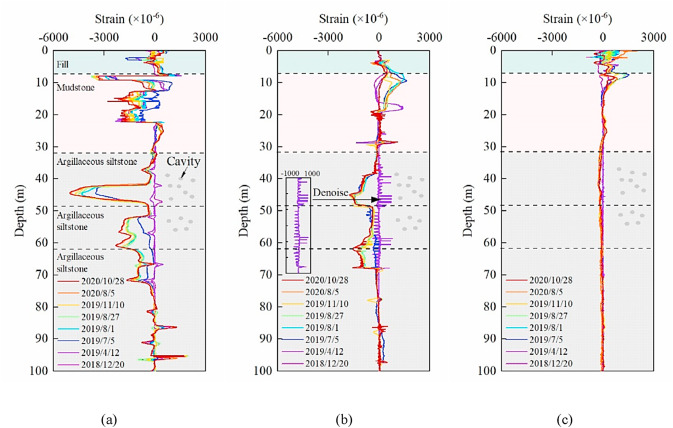
图 7.阶地区域不同光缆测得的应变曲线:(a) 定点式应变感测光缆;(b) 内定点应变感测光缆;及 (c) 金属基索状应变光缆
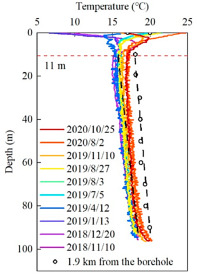
图 9.监测孔和水文钻孔中的地层温度分布对比
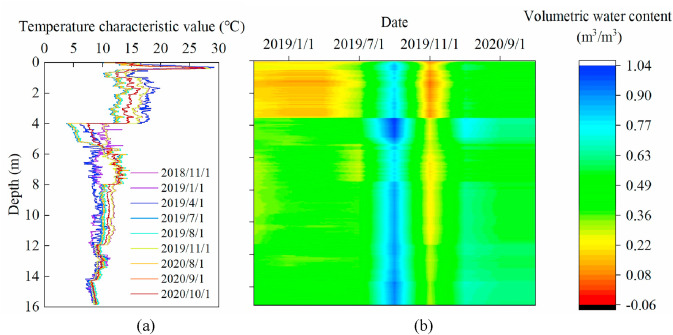
图 10.阶地区域表面的水分分布:(a) 温度特性值;(b) 表层土壤层的水分分布。
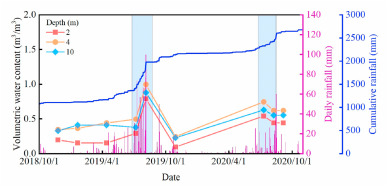
图 11.三个不同深度的含水量变化和相应的降雨数据。
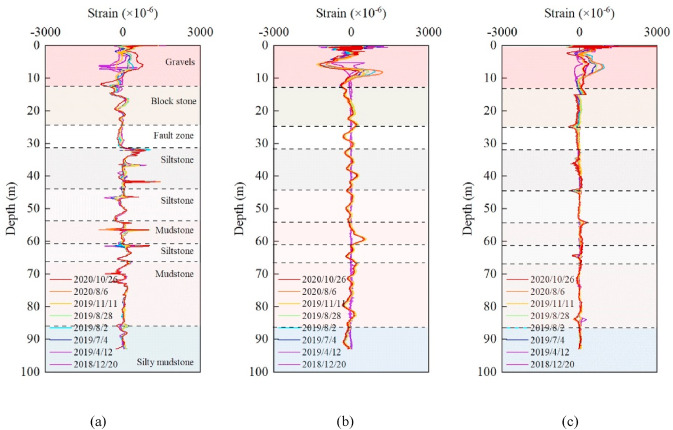
图 12.龙泉山断裂带东坡不同光缆测得的应变曲线:(a) 定点式应变感测光缆;(b) 内定点应变感测光缆;及 (c) 金属基索状应变光缆
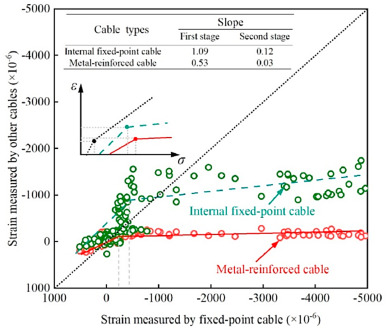
图 14.不同光缆的应变传递系数比较
本研究聚焦于四川天府新区的特殊地质条件,深入探讨了光纤神经系统(FONS)在该区域的应用潜力。两年多来,南京大学的研究者们在该地区具有不同地质特征的9个监测孔中,运用光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)、布里渊光时域反射(BOTDR)和拉曼光时域反射(ROTDR)三类先进的光纤传感技术,持续监测地层变形、温度变化及地表水文数据。基于这项研究,我们得出以下结论:
(1)现场监测结果充分证实了在地质灾害易发区域采用FONS进行地质调查的可行性。该技术能够高效捕捉地下变形、温度、水文地质特征,以及地质过程和地灾灾害的时空演变规律,展现了其在地质环境监测和地质灾害防治方面的巨大潜力。
(2)不同类型光缆在地层变形监测中的表现存在差异。为了精准监测地层结构的变形并准确获取岩土体的变形数据,选择合适的光缆类型至关重要。研究建议在钻孔中使用多种应变传感光缆,以有效评估和减少测量误差。
(3)钻孔回填工艺对确保监测数据质量具有显著影响。在钻孔回填之后,随着扰动效应逐渐减弱,光缆与周围回填材料和地层之间的耦合稳定性逐渐增强,最终达到新的平衡状态,从而确保了监测数据的准确性和可靠性。
将光纤神经系统(FONS)与云计算、大数据等尖端技术相结合,为其未来应用开辟了广阔的前景。这种技术融合极大地扩展了FONS的功能,使其从一个基础的数据收集工具转变为一个多功能的平台。人工智能和机器学习技术的融入,标志着地质监测领域的一次飞跃。这种集成不仅提高了数据处理和管理的效率,而且促进了实时信息的检索和分析。在这些技术的加持下,FONS能够执行一系列超越基础数据检索的高级功能。利用边缘计算,FONS能够在实时处理数据的同时,全面、连续地监控地质资源和地质环境条件。它能够捕捉到可能预示潜在风险的微妙变化,如滑坡、沉降或结构失稳,并提供关于地基承载状态的早期预警。这种预警机制对于预防和减轻潜在地质灾害至关重要。FONS在辅助防灾减灾决策过程和提供应急响应措施方面的能力尤为突出,这意味着它在应急响应策略和制定城市规划与建设的明智决策中扮演着关键角色,特别是在地质灾害多发区域。
FONS 的部署为在主要经济发展区(包括中国的长江三角洲和珠江三角洲)建立城市规模的监测网络提供了巨大潜力。这种扩展对于构建智慧城市和推动社会可持续发展具有重要意义。此外,FONS在促进地下空间开发和有效利用方面的潜力也将进一步被探索,这对于人口密集地区的城市发展是一个至关重要的议题。
上述成果近日以“Subsurface multi-physical monitoring of urban development zone using a fiber optic nerve system”为题,发表于工程地质领域顶级期刊《Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering》, 南京大学博士研究生王静为论文第一作者,朱鸿鹄教授和谭道远副教授为共同通讯作者,合作者包括成都地调中心王东辉、郭子奇,以及南京大学颜杜民。该工作得到了国家杰出青年科学基金项目和国家自然科学基金面上项目的资助。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2024.11.032
Subsurface multi-physical monitoring of urban development zone using a fiber optic nerve system
Jing Wanga, Donghui Wangb, Hong-Hu Zhua,c,⁎, Ziqi Guob, Dumin Yana,d, Dao-Yuan Tana,⁎⁎
a School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023, China
b Chengdu Geological Survey Center, China Geological Survey, Chengdu, 610081, China
c Engineering Research Center for Earth Sensing and Disaster Control of Jiangsu Province, Nanjing, 210023, China
d China Railway Construction Corporation Limited, Beijing, 100855, China
Abstract: The rapid expansion of urban development has led to the extensive construction of civil infrastructures. However, these urban development zones frequently face potential geohazards, primarily due to the lack of detailed site investigations and long-term monitoring of subsurface geological conditions. Understanding the temporal and spatial distributions of underground multi-field information is vital for successful engineering construction and effective utilization of urban underground space. In this study, a fiber optic nerve system (FONS) was utilized in the Tianfu New Area, Sichuan Province, China, to obtain comprehensive subsurface multi-physical information, including geological deformation, temperature, and surface hydrological data. The FONS incorporates three advanced fiber optic sensing techniques, i.e. fiber Bragg grating (FBG), Brillouin optical time domain reflectometry (BOTDR), and Raman optical time domain reflectometry (ROTDR). Fully- and quasi-distributed strain/temperature sensing cables have been installed in nine monitoring boreholes, covering various geological features such as plains, terraces, and areas within active fault zones. The field monitoring results confirm the feasibility of employing FONS for geological investigations within urban development zones, offering a valuable reference for future applications of this cost-effective technology in geohazard mitigation.
Keywords: Urban development zone, Geotechnical monitoring, Multi-physical evolution, Fiber optic sensor
References
- Benz, S.A., Irvine, D.J., Rau, G.C., et al. 2024. Global groundwater warming due to climate change. Nature Geosci. 17, 545–551.
- Cao, D.-F., Shi, B., Wei, G.-Q., Chen, S.-E., Zhu, H.-H. 2018. An improved distributed sensing method for monitoring soil moisture profile using heated carbon fibers. Measurement 123, 175-184.
- Dadashpoor, H. and Malekzadeh, N. 2020. Driving factors of formation, development, and change of spatial structure in metropolitan areas: A systematic review. J. Urban Manag. 9 (3), 286-297.
- Doherty, P., Igoe, D., Murphy, G., Gavin, K., Preston, J., Mcavoy, C., Byrne, B.W., Mcadam, R., Burd, H.J., Houlsby, G.T. 2015. Field validation of fibre Bragg grating sensors for measuring strain on driven steel piles. Geotech. Lett. 5 (2), 74-79.
- Felli, F., Paolozzi, A., Vendittozzi, C., Paris, C., Asanuma, H. 2016. Use of FBG sensors for health monitoring of pipelines. In: Proceedings of the Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems 2016. 98031L. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2222151.
- Ferraz, A., Mallet, C. Chehata, N. 2016. Large-scale road detection in forested mountainous areas using airborne topographic lidar data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 112, 23-36.
- Gabàs, A., Macau, A., Benjumea, B., Bellmunt, F., Figueras, S., Vila, M. 2014. Combination of geophysical methods to support urban geological mapping. Surv. Geophys. 35 (4), 983-1002.
- Glisic, B., Inaudi, D. 2007. Fibre Optic Methods for Structural Health Monitoring. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, NY, USA.
- Hao, M., Wang, D.H., Deng, C., He, Z.W., Zhang, J.L., Xue, D.J., Ling, X.M. 2019. 3D geological modeling and visualization of above-ground and underground integration –taking the Unicorn Island in Tianfu new area as an example. Earth Sci. Inform. 12 (4), 465-474.
- Hill, K.O., and Meltz, G. 1997. Fiber Bragg grating technology fundamentals and overview. J. Lightwave Technol. 15 (8), 1263-1276.
- Kumar, P., Mahajan, A.K., Sharma, M. 2023. Site effect assessment and vulnerability analysis using multi-geophysical methods for Kangra city, NW Himalaya, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 132, 14.
- Lai, Y., Wang, Y., Cheng, J., Chen, X., Liu, Q. 2023. Review of constraints and critical success factors of developing urban underground space. Undergr. Space 12, 137-155.
- Li, H.J., Zhu, H.H., Tan, D.Y., Shi, B., Yin, J.H. 2023. Detecting pipeline leakage using active distributed temperature Sensing: Theoretical modeling and experimental verification. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 135, 105065.
- Liu, W., Juang, C.H., Peng, Y., Chen, G. 2023. Regional characterization of vs30 with hybrid geotechnical and geological data. Undergr. Space 11, 218-231.
- Lohman, R.B., Simons, M. 2005. Some thoughts on the use of InSAR data to constrain models of surface deformation: Noise structure and data down sampling. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 6 (1).
- Osmanoğlu, B., Sunar, F., Wdowinski, S., Cabral-Cano, E. 2016. Time series analysis of InSAR data: Methods and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 115, 90-102.
- Pelecanos, L., Soga, K., Elshafie, M.Z.E.B., Battista, N.D., Kechavarzi, C., Gue, C.Y., Ouyang, Y., Seo, H.J. 2018. Distributed fiber optic sensing of axially loaded bored piles. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 144 (3), 04017122
- Peng, J.B., Huang, W.L., Wang, F.Y., et al. 2019. Geological structural classification of and geological survey method for urban underground space in China. Earth Science Frontiers 26 (3), 009-021 (in Chinese).
- Puzrin, A.M., Iten, M., Fischli, F. 2020. Monitoring of ground displacements using borehole-embedded distributed fibre optic sensors. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 53 (1), 31-38.
- Rogers, A. 1999. Distributed optical-fibre sensing. Meas. Sci. Technol. 10 (8), 75.
- Selker, J.S., Thévenaz, L., Huwald, H., Mallet, A., Luxemburg, W., Giesen, N.V.D., Stejskal, M., Zeman, J., Westhoff, M., Parlange, M.B. 2006. Distributed fiber-optic temperature sensing for hydrologic systems. Water Resour. Res. 42, 1-8.
- Siebenmann, R., Yu, H.-T., Bachus, R. 2015. UCIMS: Advances in geotechnical construction and performance monitoring. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 7 (2), 207-212.
- Tyler, S.W., Selker, J.S., Hausner, M.B., Hatch, C.E., Torgersen, T., Thodal, C.E., and Schladow, S.G. 2009. Environmental temperature sensing using Raman spectra DTS fiber-optic methods. Water Resour. Res. 45, 1-11.
- von der Tann, L., Sterling, R., Zhou, Y., Metje, N. 2020. Systems approaches to urban underground space planning and management – A review. Undergr. Space 5 (2), 144-166.
Wang, J., Zhu, H.-H., Tan, D.-Y., Li, Z.-L., Li, J., Wei, C., Shi, B. 2023. Thermal integrity profiling of cast-in-situ piles in sand using fiber-optic distributed temperature sensing. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 15 (12), 3244-3255. - Wang J, Lin S Q, Tan D Y, et al. 2024. A novel method for integrity assessment of soil-nailing works with actively heated fiber-optic sensors. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 150 (8), 04024063.
- Xu, Q., Dong, X.J., Li, W.L. 2019. Integrated space air ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 44 (7), 957-966 (in Chinese).
- Ye, X., Zhu, H.H., Chang, F.N., Xie, T.C., Tian, F., Zhang, W., Catani, F. 2024. Revisiting spatiotemporal evolution process and mechanism of a giant reservoir landslide during weather extremes. Eng. Geol. 332, 107480.
- Ye, X., Zhu, H.H., Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Shi, B., Schenato, L., Pasuto, A. 2022. Subsurface multi-physical monitoring of a reservoir landslide with the fiber-optic nerve system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 49 (11), e2022GL098211.
- Zeng, C., Liu, Y.L., Stein, A., Jiao, L.M. 2015. Characterization and spatial modelling of urban sprawl in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 34, 10-24.
- Zeni, L. Picarelli, B. Avolio, A. Coscetta, R. Papa, G. Zeni, C. Di Maio, R. Vassallo, A. Minardo. 2015. Brillouin optical time-domain analysis for geotechnical monitoring. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 7 (4), 458-462.
- Zhang, X., Zhu, H., Jiang, X., Broere, W. 2024. Distributed fiber optic sensors for tunnel monitoring: A state-of-the-art review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 16 (9), 3841-3863.
- Zhu, H., Huang, X., Li, X., Zhang, L., Liu, X. 2016. Evaluation of urban underground space resources using digitalization technologies. Undergr. Space 1 (2), 124-136.
- Zhu, H.H., Wang, J.C., Reddy, N.G., Garg, A., Cao, D.F., Liu, X.F., Shi, B. 2024a. Monitoring infiltration of capillary barrier with actively heated fibre Bragg gratings. Environ. Geotech. 11(7): 502–517.
- Zhu, H.-H., Ye, X., Pei, H.-F, Zhang, W., Cheng, G., Li, Z.-L. 2024b. Probing multi-physical process and deformation mechanism of a large-scale landslide using integrated dual-source monitoring. Geosci. Front. 15 (2): 101773.
- Zhuang, Y., Xing, A. 2022. History must not repeat itself-urban geological safety assessment is essential. Nat. Hazards. 111, 2141–2145.
- Zhuang, C., Zhu, H.H., Wang, W., Liu, B.H., Ma, Y.H., Guo, J., Liu, C.H., Zhang, H.P., Liu, F., Cui, L.L. 2023. Research on urban 3D geological modelling based on multi-modal data fusion: a case study in Jinan, China. Earth Sci. Inform. 16, 549–563.
