【背景介绍】
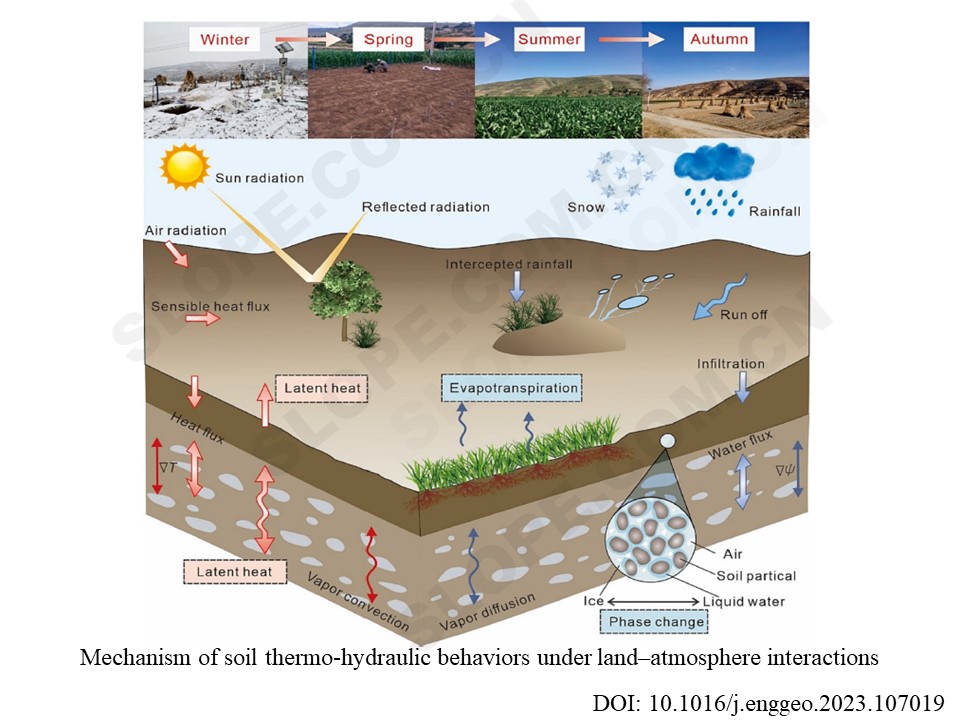
土壤是地球生态系统的重要组成部分,在陆地-大气相互作用中起着至关重要的作用。然而,理解土壤热-水(T-H)参数(如温度和湿度)的复杂行为仍然是一个挑战。这些知识对于解读潜在的地质灾害和发展可持续的土地管理实践至关重要。中国黄土高原是季节性冻土区,是研究th行为的理想场所。研究人员开发了一种新型的光纤传感系统,能够以高时空分辨率和精度连续测量土壤TH参数。
【研究内容】
研究人员开发的光纤传感系统结合了主动加热光纤光栅(AH-FBG)和人工神经网络(ANN)技术。用于在中国黄土高原进行岩土仪器测试,并分析9个月的监测数据。数据揭示了季节性冻结黄土在不同深度和水迁移阶段的TH行为的不同模式。研究表明,冰水相变、潜热和热对流对黄土中的热量和质量输送有显著影响。气温被确定为表征部分冻结黄土中TH行为的主要大气因素,而降雨和气温在未冻结黄土中具有双重效应。
【研究意义】
本研究是在考虑水分和温度不均匀性的情况下获取原状黄土TH参数的早期尝试。这些发现为陆地-大气相互作用提供了独特的见解,为解读潜在地质灾害的触发因素提供了有价值的信息。研究人员开发的光纤传感系统有可能彻底改变土壤TH参数测量,促进可持续土地管理实践。
作者:Wu B.; Zhu H.-H.; Cao D.-F.; Liu X.-F.; Liu T.-X.
出版时间:2023-03-20
来源:Engineering Geology 315 (2023) 107019
DOI:10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107019
************
Fiber optic sensing-based field investigation of thermo-hydraulic behaviors of loess for characterizing land-atmosphere interactions
Abstract: Understanding soil thermo-hydraulic (TH) behaviors requires ample and reliable soil property information. However, it is still challenging to measure in-situ TH parameters with high spatiotemporal resolution and accuracy. Herein, a fiber optic sensing system was developed by combining actively heated fiber Bragg grating (AHFBG) and artificial neural network (ANN) technologies, which enables continuous measurement of spatiotemporal variations in TH parameters of in-situ soil. Geotechnical instrumentation was conducted on the Loess Plateau, China, by using the newly developed system. Analyses of 9-month monitoring data allow us to pinpoint diverse patterns of TH behaviors of seasonally frozen loess at various depths and water migration stages. The significant impacts of ice-water phase change, latent heat, and heat convection on heat and mass transport in loess are especially demonstrated. The air temperature was further identified as the main atmospheric factor for characterizing TH behaviors in partially frozen loess, while both rainfall and air temperature have dual effects in unfrozen loess. The field investigation here presents an early attempt to acquire TH parameters of in-situ loess considering the moisture and temperature inhomogeneity. The findings in this study offer unique insights into land–atmosphere interactions, providing valuable information for deciphering triggers of potential geohazards.
Keywords: Actively heated fiber Bragg grating (AH-FBG), Artificial neural network (ANN), Thermo-hydraulic behavior, Land–atmosphere interaction, Field monitoring, Loess
