【研究背景】
社会上的一些问题,例如建筑物的安全性和桥梁的耐久性,需要使用新的技术来解决。然而,目前的研究领域存在一个挑战,即如何准确地测量裂纹的大小和数量。这是一个重要的问题,因为它可以帮助人们预测材料的寿命和安全性,并采取必要的措施来保护人们的生命和财产。
【研究内容】
本研究旨在解决裂纹量化的问题。研究人员通过进行板分裂试验,探究了裸光纤和其涂层层之间的界面剪切应力-滑移关系。基于此,他们提出了一种基于界面断裂能的分析模型,将界面剪切应力-滑移关系转换为微观和宏观裂纹的COD。研究人员通过板分裂试验和文献中的实验数据验证了模型的准确性。此外,他们还利用四点梁试验的实验结果研究了模型在多裂纹情况下的可行性。模型辅以应变叠加策略,在界面剥离之前精确量化多个裂纹的COD,但在界面剥离之后则失败了。此外,他们还提出了一种基于裂开长度和相应COD之间线性关系的简化方法,便于评估剥离后的COD。
【研究意义】
本研究提出了一种新的方法,可以更准确地测量裂纹的大小和数量。这种方法可以应用于建筑物、桥梁等结构的监测和维护,有助于预测材料的寿命和安全性,并采取必要的措施来保护人们的生命和财产。此外,该研究还提出了一种简化方法,使得COD的评估更加容易和高效。这些创新点都具有重要的研究意义和应用价值。
来源:Structural Health Monitoring
作者:Lin, Shaoqun, Tan, Daoyuan, Jian-Hua, Yin, Zhu, Honghu, Yong, Kong
机构:香港理工大学,南京大学
*****
Distributed fiber optic sensing for micro- and macro-crack quantification: an interfacial-fracture-energy-based model
Authors: Shao-Qun Lin, Dao-Yuan Tan, Jian-Hua Yin, Hong-Hu Zhu, Yong Kong
Affiliations: Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China; School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
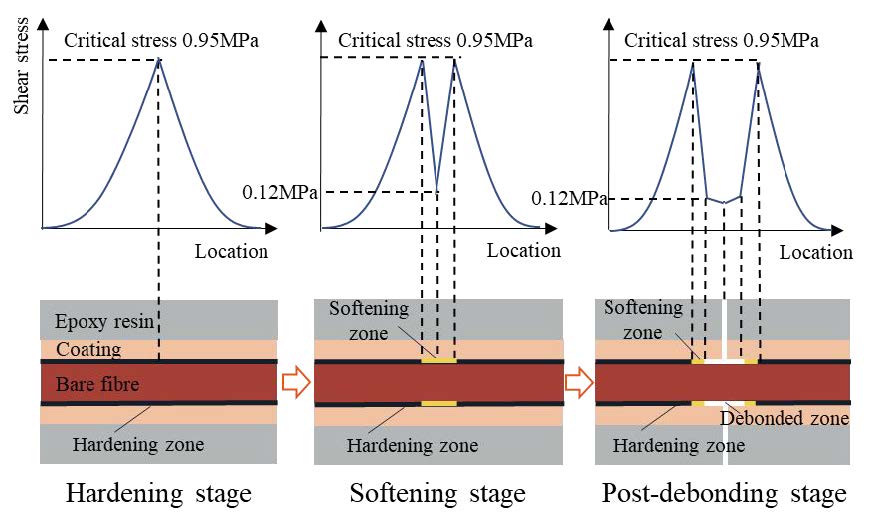
[Abstract] Clarifying the strain transfer between the host material with a crack opening displacement (COD) and the optical fiber after interfacial debonding remains a critical challenge for crack quantification. The interfacial debonding induced a triangular form strain profile around the crack due to the residual shear stresses at the interface. This study investigated the interfacial shear stress-slip relationship between the bare fiber and its coating layer through a plate splitting test. Based on that, we proposed an interfacial-fracture-energy-based analytical model to convert distributed fiber optic strains before and after interfacial debonding to CODs of micro- and macro-cracks. The accuracy of the model under a single crack was validated through plate splitting tests and the experimental data reported in the literature. Furthermore, experimental results from a four-point beam test were utilized to investigate the feasibility of the model under multiple cracks. The model, assisted by the strain superposition strategy, accurately quantified the CODs of multiple cracks before interfacial debonding but failed when interfacial debonding occurred. In addition, we proposed a simplified method based on the linear relationship between the debonded lengths and the corresponding CODs, which facilitates evaluation of the CODs after debonding.
References
1. Hoult NA, Ekim O, Regier R. Damage/deterioration detection for steel structures using distributed fiber optic strain sensors. J Eng Mech 2014; 140(12): 04014097. Crossref Google Scholar
2. Regier R, Hoult NA. Concrete deterioration detection using distributed sensors. ICE Proc Struct Build 2015; 168(2): 118–126. Crossref Google Scholar
3. Berrocal CG, Fernandez I, Rempling R. The interplay between corrosion and cracks in reinforced concrete beams with non-uniform reinforcement corrosion. Mater Struct 2022; 55(4): 120. Crossref Google Scholar
4. Zhao L, Tang F, Verstrynge E, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation into corrosion-induced mortar/concrete cracking with distributed optical fiber sensors. J Civ Struct Health Monit 2022; 12(4): 943–960. Crossref Google Scholar
5. Lin S-Q, Tan D-Y, Yin J-H, et al. A novel approach to surface strain measurement for cylindrical rock specimens under uniaxial compression using distributed fibre optic sensor technology. Rock Mech Rock Eng 2021; 54: 6605–6619. Crossref Google Scholar
6. Zhang P, Yin ZY. A novel deep learning-based modelling strategy from image of particles to mechanical properties for granular materials with CNN and BiLSTM. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2021; 382: 113858. Crossref Google Scholar
7. Xu J-J, Tang C-S, Cheng Q, et al. Monitoring and early detection of soil desiccation cracking using distributed fiber optical sensing. Géotechnique. Epub ahead of print 5 July 2022. Crossref Google Scholar
8. Li H-J, Zhu H-H, Zhang C-X, et al. Monitoring flexure behavior of compacted clay beam using high-resolution distributed fiber optic strain sensors. Geotech Testing J 2022; 45(3): 20200331. Crossref Google Scholar
9. Domaneschi M, Niccolini G, Lacidogna G, et al. Nondestructive monitoring techniques for crack detection and localization in RC elements. Appl Sci 2020; 10(9): 3248. Crossref Google Scholar
10. Okabe Y, Tanaka N, Takeda N. Effect of fiber coating on crack detection in carbon fiber reinforced plastic composites using fiber Bragg grating sensors. Smart Mater Struct 2002; 11(6): 892. Crossref ISI Google Scholar
11. Zhang S, Liu H, Coulibaly AAS, et al. Fiber optic sensing of concrete cracking and rebar deformation using several types of cable. Struct Control Health Monit 2020; 28(2): e2664. Google Scholar
12. Grunicke UH, Lienhart W, Vorwagner A. Long-term monitoring of visually not inspectable tunnel linings using fibre optic sensing. Geomech Tunnell 2021; 14(1): 19–32. Crossref Google Scholar
13. Ye X, Zhu H-H, Wang J, et al. Subsurface multi-physical monitoring of a reservoir landslide with the fiber-optic nerve system. Geophys Res Lett 2022; 49: e2022GL098211. Crossref Google Scholar
14. Wang DY, Zhu H-H, Wang J, et al. Characterization of sliding surface deformation and stability evaluation of landslides with fiber–optic strain sensing nerves. Eng Geology 2023; 314: 107011. Crossref Google Scholar
15. Zhu H-H, Wang D-Y, Shi B, et al. Performance monitoring of a curved shield tunnel during adjacent excavations using a fiber optic nervous sensing system. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 2022; 124: 104483. Crossref Google Scholar
16. Ansari F, Yuan L. Mechanics of bond and interface shear transfer in optical fiber sensors. J Eng Mech 1998; 124(4): 385–394. Crossref ISI Google Scholar
18. Li H-N, Zhou G-D, Ren L, et al. Strain transfer coefficient analyses for embedded fiber Bragg grating sensors in different host materials. J Eng Mech 2009; 135(12): 1343–1353. Crossref Google Scholar
19. Tan X, Bao Y, Zhang Q, et al. Strain transfer effect in distributed fiber optic sensors under an arbitrary field. Autom Constr 2021; 124: 103597. Crossref Google Scholar20. Chapeleau X, Bassil A. A general solution to determine strain profile in the core of distributed fiber optic sensors under any arbitrary strain fields. Sensors 2021; 21(16): 5423. Crossref Google Scholar
21. Imai M, Feng M. Sensing optical fiber installation study for crack identification using a stimulated Brillouin-based strain sensor. Struct Health Monit 2012; 11(5): 501–509. Crossref ISI Google Scholar
22. Feng X, Zhou J, Sun C, et al. Theoretical and experimental investigations into crack detection with BOTDR-distributed fiber optic sensors. J Eng Mech 2013; 139(12): 1797–1807. Crossref ISI Google Scholar23. Bassil A, Chapeleau X, Leduc D, et al. Concrete crack monitoring using a novel strain transfer model for distributed fiber optics sensors. Sensors 2020; 20(8): 2220. Crossref Google Scholar
24. Zhang S, Liu H, Cheng J, et al. A mechanical model to interpret distributed fiber optic strain measurement at displacement discontinuities. Struct Health Monit 2020; 20(5): 2584–2603. Crossref Google Scholar
25. Billon A, Hénault J-M, Quiertant M, et al. Qualification of a distributed optical fiber sensor bonded to the surface of a concrete structure: a methodology to obtain quantitative strain measurements. Smart Mater Struct 2015; 24(11): 115001.
26. Zhao L, Tang F, Li H.-N, et al. Characterization of OFDR distributed optical fiber for crack monitoring considering fiber-coating interfacial slip. Struct Health Monit 2022; 22(1): 180–200. Crossref Google Scholar27. Ye H, Liu J, Zhou Y, et al. Crack detection and retardation of steel structure by smart CFRP embedding PPP-BOTDA fiber sensors. J Building Eng 2022; 49: 104018. Crossref Google Scholar28. Ye H, Liu J, Zhou Y, et al. Monitoring of crack opening displacement of steel structure by PPP-BOTDA-distributed fiber optical sensors: theory and experiment. Eng Fracture Mech 2022; 262: 108275. Crossref Google Scholar
29. Wang C, Olson M, Doijkhand N, et al. A novel DdTS technology based on fiber optics for early leak detection in pipelines. In 2016 IEEE international carnahan conference on security technology (ICCST), Orlando, FL, USA, 2016. IEEE.Crossref Google Scholar
30. Sieńko R, Zych M, Bednarski Ł, et al. Strain and crack analysis within concrete members using distributed fibre optic sensors. Struct Health Monit 2019; 18(5–6): 1510–1526. Crossref ISI Google Scholar
31. Berrocal CG, Fernandez I, Rempling R. Crack monitoring in reinforced concrete beams by distributed optical fiber sensors. Struct Infrastruct Eng 2020; 17(1): 124–139. Crossref Google Scholar
32. Tan X, Abu-Obeidah A, Bao Y, et al. Measurement and visualization of strains and cracks in CFRP post-tensioned fiber reinforced concrete beams using distributed fiber optic sensors. Autom Constr 2021; 124: 103604. Crossref Google Scholar
33. Fernandez I, Berrocal CG, Almfeldt S, et al. Monitoring of new and existing stainless-steel reinforced concrete structures by clad distributed optical fibre sensing. Struct Health Monit 2023; 22(1): 257–275. Crossref Google Scholar
34. Tan X., Bao Y. Measuring crack width using a distributed fiber optic sensor based on optical frequency domain reflectometry. Measurement 2021; 172, 108945. Crossref Google Scholar
35. Bassil A. Distributed fiber optics sensing for crack monitoring of concrete structures. Doctoral dissertation, Université de Nantes, 2019. Google Scholar
37. Zhu H-H, She J-K, Zhang C-C, et al. Experimental study on pullout performance of sensing optical fibers in compacted sand. Measurement 2015; 73: 284–294. Crossref Google Scholar
38. Meng D, Ansari F, Feng X. Detection and monitoring of surface micro-cracks by PPP-BOTDA. Appl Optics 2015; 54(16): 4972–4978. Crossref PubMed Google Scholar
39. Duck G, Leblanc M. Arbitrary strain transfer from a host to an embedded fiber-optic sensor. Smart Mater Struct 2000; 9(4): 492. Crossref ISI Google Scholar
41. Kim S-W, Jeong M-S, Lee I, Kim, et al. Determination of the maximum strains experienced by composite structures using metal coated optical fiber sensors. Compos Sci Technol 2013; 78: 48–55. Crossref Google Scholar
47. Ho HC, Chung KF, Liu X, et al. Modelling tensile tests on high strength S690 steel materials undergoing large deformations. Eng Struct 2019; 192: 305–322. Crossref Google Scholar
48. Hu YF, Chung KF, Jin H, et al. Structural behaviour of T-joints between high strength S690 steel cold-formed circular hollow sections. J Constr Steel Res 2021; 182: 106686. Crossref Google Scholar
